Ensemble Learning is a method used in Machine Learning that consists of combining multiple models. These models are “base models” or “weak learners”. Weak learners are models that don’t have a good performance, for example, they have high variance or high bias.
There are two kinds of ensemble models:
- Homogeneous: based on a combination of a single type of base models
- Heterogeneous: based on multiple types of base models
There are three methods to combine base models:
- Bagging
- Boosting
- Stacking
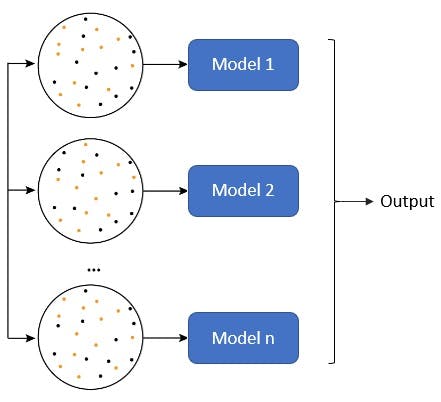
Bagging
It stands for “bootstrap aggregating”. It employs several homogeneous weak learners that have a high variance, with the objective of reducing the variance. Each weak learner is trained with a bootstrapped dataset. This means that an arbitrary number of samples are randomly and independently drawn from the training dataset for each weak learner model.
The inference is made differently depending on the type of model:
- Regression: the inference is the average of each model’s prediction
- Classification: it could be by hard-voting in which the inference is decided by the prediction made by the majority of the models; or soft-voting in which the inference is based on the average of the probabilities predicted by each weak learner.
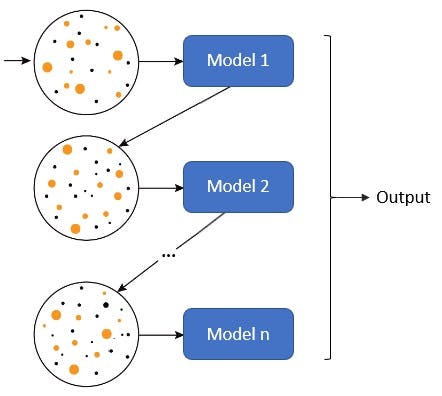
Boosting
It uses several homogeneous weak learners with low variance and high bias to reduce the bias. The base models are trained sequentially. Each model is trained giving more importance to those samples badly handled by the previously trained models in the sequence.
There are several ways of making the inference:
- Average of the predictions of the weak learners
- Weighted sum of predictions
There are three popular algorithms based on boosting:
- AdaBoost
- Gradient Boosting
- XGBoost
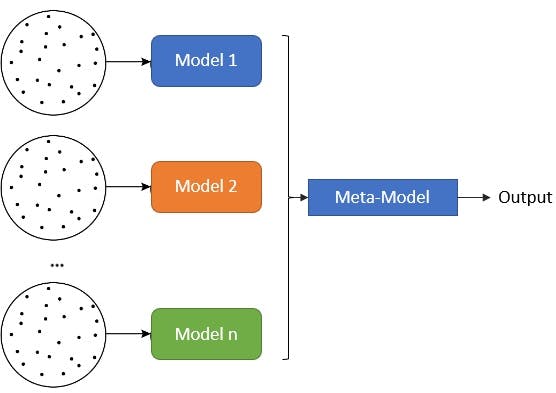
Stacking
It uses heterogeneous weak learners and a meta-model. The weak learners output their predictions and these are taken as input for the meta-model, which aggregates them and makes the final inference.
These models are generally trained using a k-fold cross-training, meaning that the training dataset is split into k folds or groups. k-1 of these folds are used to train the weak learners, while the remaining one is used to train the meta-model. This process is then repeated iteratively.
If you liked this content don't forget to follow me here and on Twitter!


